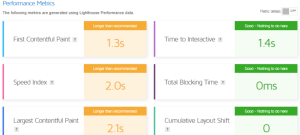
Fast loading (rendering) of a Web page is a must in today’s age. Most websites perform a basic checklist to make your website faster. There are tools such as Page Speed Insights from Google, GTMetrix or Webpagetest that checks your website and suggests what can be improved so that the website displays faster.
When it comes to page speed, the main things most developers do are reduce (minify) files, gzip files and compress images.
At a more advanced level, there are steps such as caching, using a CDN to distribute the resources (which is recommended if you have visitors from abroad), code splitting, eliminating JavaScript blocks, etc.
But there are other techniques that most people don’t talk about when they talk about making your Web page faster. These performance enhancing techniques are commonly known as Resource Hints (prefetching techniques). It’s a simple way of telling the browser – Hello browser, I will definitely need resources A, B and C at some point. So prefetch that now, so we can quickly serve it later when requested.
The execution takes place in the idle time of the browser, which is the moment when the browser has already loaded the page and is doing nothing. This means that when a visitor is reading your page or blog post, the browser loads another page in the background and calculates its display. This way, the page is displayed faster as soon as the corresponding link is clicked. In other words, pre-fetch and pre-render.
If you use Google Analytics, you can find out how visitors navigate through your website to make the best use of these techniques.
The following Resource Hints can be used: dns-prefetch, prefetch, pre-connect and pre-render.
DNS-Prefetch
A dns-prefetch tells the browser that we need a few sources of a particular URL so that the browser can start DNS handling as quickly as possible.
<link rel=”dns-prefetch” href=”//een-website.nl”>Suppose at some point within the website we are redirected to a-website.co.uk. We can add the above line in the head of the website. After the browser parses the document, it starts DNS handling for a-website.co.uk. This will make the further requests for one-website.co.uk a little faster.
Using DNS prefetch can save a lot of time with redirects and on mobile devices or locations where Internet speed is slower.
Link Prefetch
A prefetch is used when we are sure that a particular resource will be used by the visitor at some point. Do not confuse dns-prefetch and prefetch, as both are used for different reasons. A common use case is to prefetch images that can be requested at a certain point. Once the page is loaded, the browser begins fetching the image at, for example: example.com/images/logo.jpg
A prefetch looks like this:
<link rel=”prefetch” href=”http://voorbeeld.nl/afbeeldingen/logo.jpg">When this line occurs, the browser requests the image from the specified URL, downloads it and stores it in the browser cache.
Be careful not to prefetch too many or too large sources, your browser may then give you the following error message:
Failed to load resource: net::ERR_CACHE_WRITE_FAILUREThis means that the resource we were trying to prefetch is too large to write to the browser cache. Only use prefetch if you are absolutely sure that the resource will be used at some point.
Pre-connect
For a browser, actions such as DNS handling (translating ip addresses to domain names), TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) handshake and TLS (Transport layer security) handling are relatively black tasks.
Pre-connect is similar to a DNS prefetch, but also optionally performs the TCP handshake and TLS handoffs. This saves user time by eliminating these actions.
By including the following code in the main body of your website, you can connect a web page in advance.
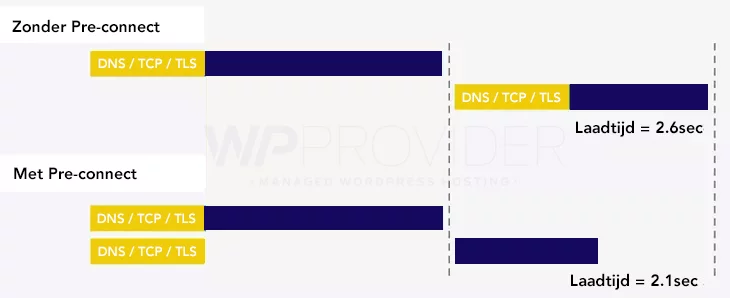
Pre-render
Pre-render is the supreme boss of all prefetching techniques and should be used carefully. Pre-render instructs the browser to prefetch all sources of a given page with the code below:
<link rel=”prerender” href=”https://voorbeeld.nl/bepaalde-pagina">In fact, at https://voorbeeld.nl/bepaalde-pagina the page is invisibly loaded and saved by the browser. When the visitor navigates to this page then the browser can easily load the pre-rendered page, providing a better user experience.
Here, it is important that you do not apply this unnecessarily because it is more likely to cause problems (unnecessary resources) than a faster page.
How do I apply this?
Are you using our Managed WordPress package? Then you don’t have to do this yourself, we take care of all the worries for you.
Website remains slow?
It is not said that only these techniques make the website lightning fast, of course it is important that the basis (the web hosting) of your website is good. Are you not yet hosting with WP Provider? Get in touch to discuss options.